Torque Sensing for Harmonic Drive Robotics Actuators
This industry-sponsored capstone project developed a high-precision underwater torque sensing system for Houston Mechatronics' Aquanaut subsea robot. The system needed to operate reliably at depths up to 300m while maintaining measurement accuracy for the robot's 7-DOF manipulator arms in harsh underwater environments.
Contributions:
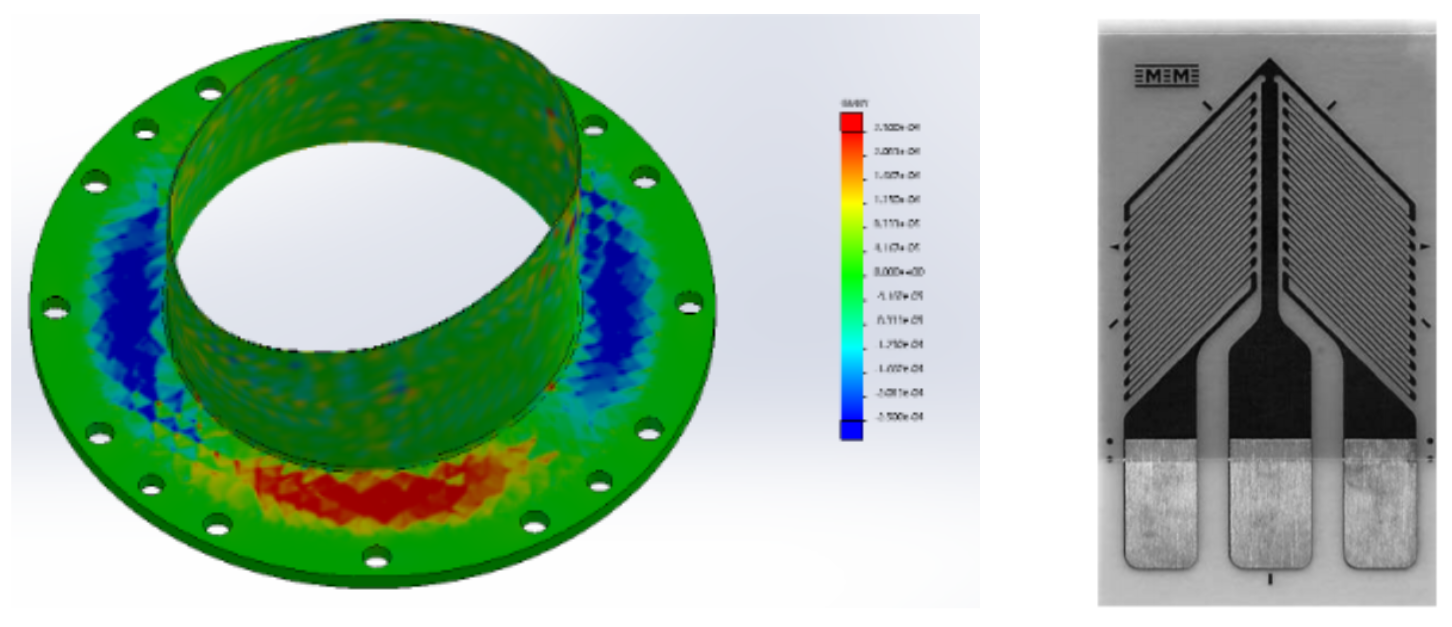
Led 6-person interdisciplinary team to develop underwater torque sensing system, achieving 8% accuracy at 950Nm torque capacity and 300m depth rating
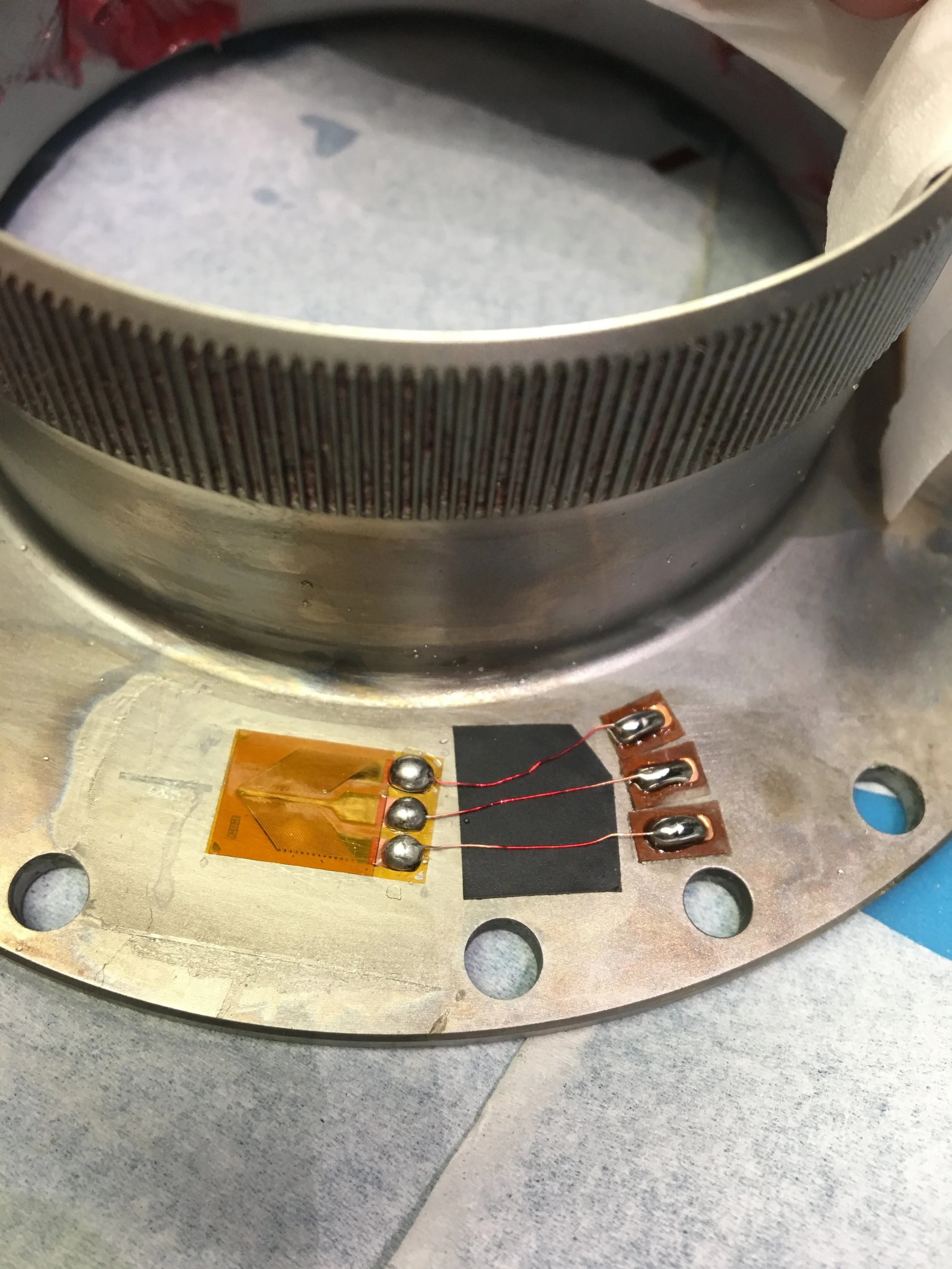
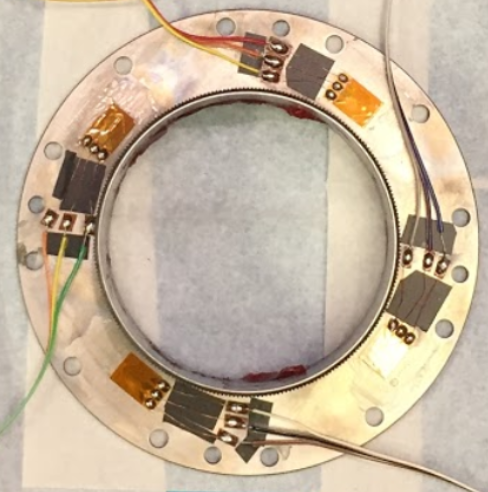
Designed and implemented strain gauge integration including sensor application, wiring harnesses, and signal conditioning circuits for subsea applications
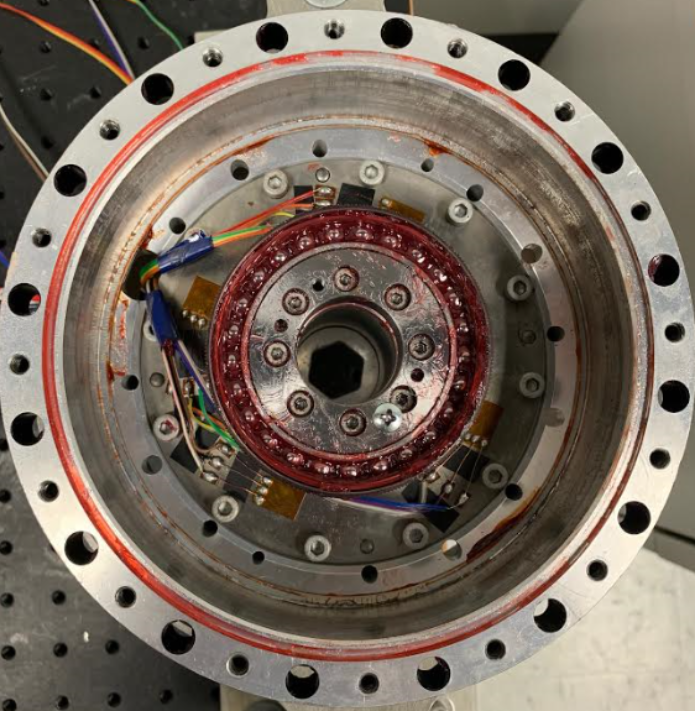
Developed comprehensive testbed for performance validation, integrating pressure testing capabilities and data acquisition systems
Coordinated project execution across multiple stakeholders including HMI engineers and strain gauge vendors
Awarded "Best Robotics Project" award at Rice Engineering Design Showcase 2019
Collaborators: Zachary Anderson, Nicholas Jeffress, Joel (Sung) Kim, Eugenio Mesta, Jacob Rupp